- Calcaneal fractures are the most common tarsal fractures, Approximately 75% are intra-articular
- Sanders Classification is used for calcaneum fractures
- Traumatic axial loading is the primary mechanism of injury, Fall from height, Motor-vehicle accidents are causes for calcaneal fractures
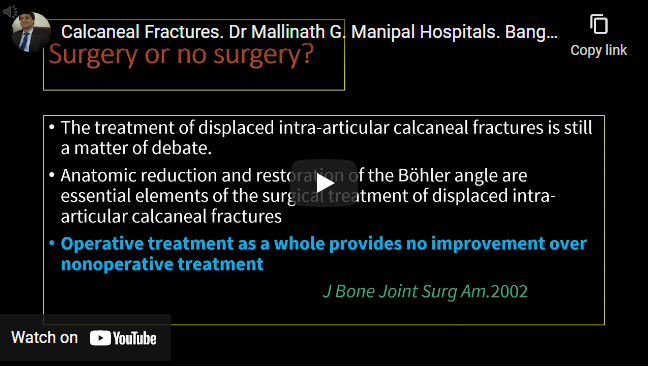
- Displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures (i.e., ≥2 mm of articular incongruity at the posterior facet or a Bohler angle of <20°), Open fractures, Displaced posterior tuberosity component tenting the skin all need surgical fixation
- Peripheral vascular disease, Poorly controlled diabetes , Medical comorbidities, History of nicotine use, Poor soft-tissue status, Nonambulatory status etc are relative contraindications
- Percutaneous Reduction, Screw Fixation, and Calcium Sulfate Cement Grafting
- Operative treatment was associated with a higher risk of complications but a reduced prevalence of posttraumatic arthritis