- Recurrence of instability is glenoid bone loss
- ≥30% bone loss in the glenoid need bone graft
- Bone defect involving > 21% glenoid decreases force required to subluxation
- Latarjets procedure increases the stability by restoring the AP diameter, sling effect to support the anteroinferior aspect of the capsule and dynamic contraction of the conjoined muscles
- Screw in the coracoid process is directed at <10° (α) from the glenoid surface to avoid injury to the suprascapular nerve
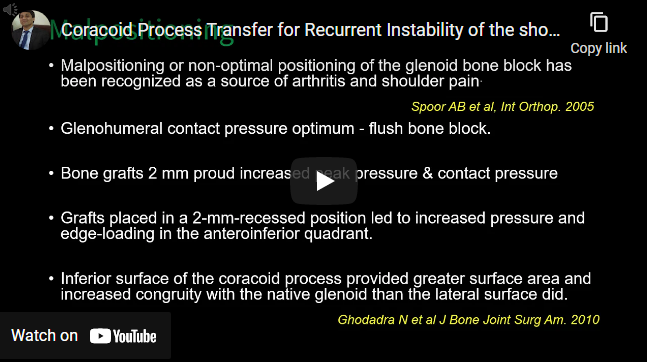
- Malpositioning or non-optimal positioning of the glenoid bone block has been recognized as a source of arthritis and shoulder pain
- Engaging Hill-Sachs lesion is one in which the humeral head defect aligns with the anterior edge of the glenoid in abduction and external rotation, leading to shoulder dislocation
- If hill sachs >37.5%, then it needs bone graft