- Coronal curve >10° with rotation
- Affects 1% to 3% of children, female to male ratio for curves > 30° is 9:1
- Amount of skeletal growth remaining determines the curve magnitude
- Etiology is thought to be autosomal dominant, however its still unclear
- Presents with limb leng discrepancy, shoulder and pelvis asymmetry, rib hump
- Cobbs angle >100 on an x ray is diagnostic
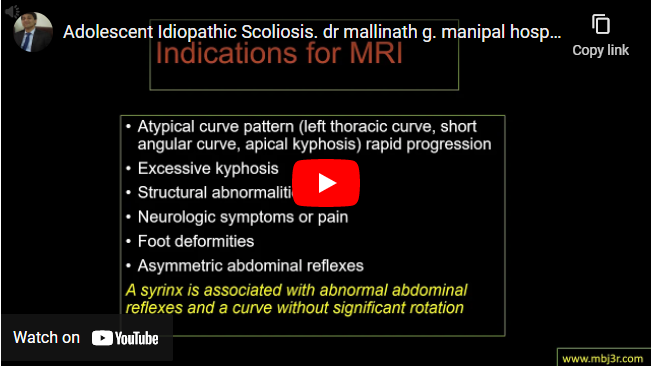
- Atypical curve pattern (left thoracic curve, short angular curve, apical kyphosis) rapid progression, Excessive kyphosis, Structural abnormalities, Neurologic symptoms or pain, Foot deformities, Asymmetric abdominal reflexes etc warrant MRI
- Cobbs angle <250 requires observation whereas angle between 25-400 can be treated with a brace
- Lumbar curves have a higher chance of success with brace wear than thoracic curves
- Posterior-only approaches most common technique and Lenke systems are most widely used system