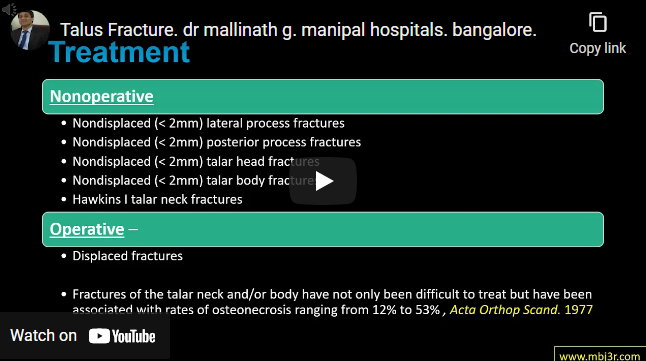
Nonsurgical management of hindfoot arthritis includes oral anti-inflammatories, steroid injections, and bracing Progressive condition, hindfoot arthritis typically requires arthrodesis Patient with prior calcaneum fracture need special attention while doing subtalar arthrodesis Maintain height subtalar joint area with graft Isolated talonavicular arthritis typically occurs in the setting of rheumatoid arthritis or Mueller-Weiss disease Subtalar and talonavicular arthrodeses typically done for adult-acquired…