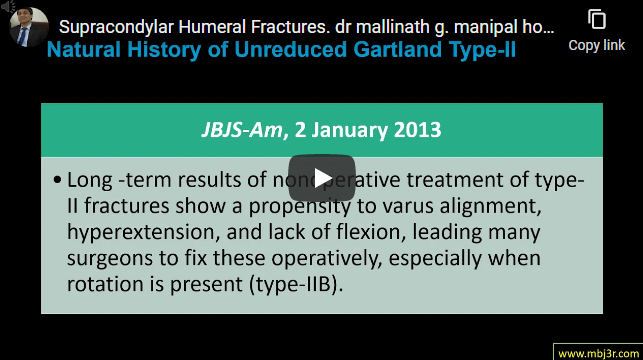
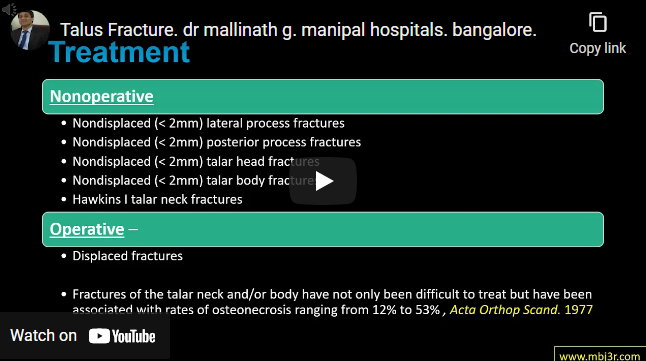
Cervical spine is commonly affected in RA Following involvement is seen in decreasing order: Anterior atlontoaxial subluxation, atlantoaxial subluxation combined with subaxial Subluxation, Isolated subaxial subluxation, Superior migration of odontoid (a/k/a basilar invagination or vertical atlontoaxial instability Present with neck pain and paraesthesia / numbness in upper/lower extremities X rays are useful in identifying cervical spine changes Non operative management…