Moderate to high-energy trauma 8% to 43% of these are open fractures and Ligament disruption seen in 43% to 80% CT scan is done to assess the articular collapse and fracture comminution Schatzker classification is commonly used Treatment is often aimed at restoring the articular congruity, coronal alignment and angular stability Open reduction and internal fixation is the traditional means…
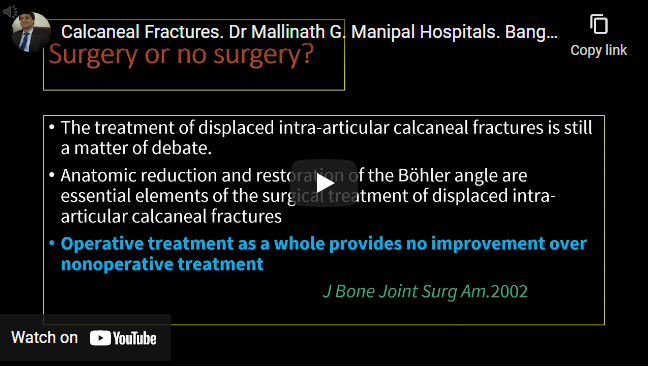
Calcaneal fractures are the most common tarsal fractures, Approximately 75% are intra-articular Sanders Classification is used for calcaneum fractures Traumatic axial loading is the primary mechanism of injury, Fall from height, Motor-vehicle accidents are causes for calcaneal fractures Displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures (i.e., ≥2 mm of articular incongruity at the posterior facet or a Bohler angle of <20°), Open fractures, Displaced posterior…

Damage control orthopaedics is an approach that contains and stabilizes orthopaedic injuries so that the patient’s overall physiology can improve It focuses on control of hemorrhage, management of soft-tissue injury, achievement of provisional fracture stability, avoiding additional insults to the patient It remains a clinical decision when to shift from early total care to damage control orthopaedics Days 2, 3,…

It is a systemic manifestation of fat emboli in the circulation seen mostly after long bone fractures Triad of findings: hypoxia, confusion, and petechia. Young obese males more affected especially following femur shaft fracture The fat cells exhibit inflammatory properties that leads to ARDS Gurds and Wilsons criteria is used to diagnose FES Chest X ray reveals snow storm appearance …

Stabilize the patient before you investigate Operative options include intramedullary nailing, ex-fix and plating Indications for retrograde nailing are: ipsilateral acetabular/neck fracture, floating knee, distal end fracture, morbid obesity etc Platting indications: deformed femur, neck fracture, pregnancy, narrow canal, impending FES Reaming not an issue in trauma patients without chest injuries who have been well resuscitated Benefits of reaming include…

greater remodelling potential Galeazzi and Monteggia are common fractures Diaphyseal fractures : long arm cast with acceptable reduction consists of angulation <15°and alignment of the proximal and distal rotational landmarks Proximal-third radius fractures are the hardest to control nonoperatively Surgical fixation for unacceptable reduction with plates or intramedullary nails is accepted Plates : higher complication rates and difficult to remove
