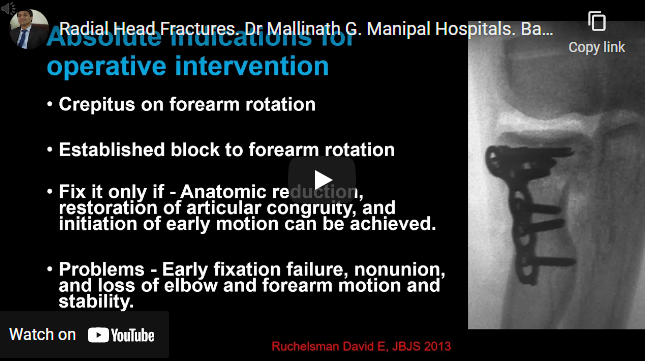
The radial head is an important stabilizer for valgus, axial, and posterolateral rotational forces Mason classification Conservative management for Isolated stable Mason type-1 or type-2 fracture of the radial head or neck Indications for operative management are crepitus on movement bone block Surgical exposure: kocher’s approach Low profile plate and headless screws used Protect PIN Radial head excision typically not…